You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Example 1:
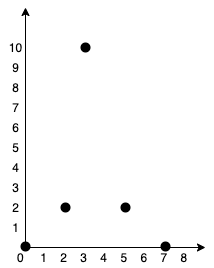
Input: points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
Output: 20
Explanation:
We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20.
Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
Output: 18
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 1000- $
-10^6$ <= xi, yi <= $10^6$ - All pairs
(xi, yi)are distinct.
給定一個整數矩陣 points, 其中每個 entry points[i] = [$x_i, y_i]$ 代表 2 維平面上的座標點
定義平面上認兩點 points[i], points[j] 的 manhattan dist 為
要求寫一個演算法算出要連接所有座標點
並且唯一通過所有點一次所需要花費的最小 manhattan dist 總和
這題目相當於要找出在 2 維座標點上的 Minimum Spanning Tree
要找出 Minimum Spanning Tree 的 Cost
可以透過 Prim’s algorithm
這個演算法直觀來看就是先以每個點為起點計算每兩點之間的 Cost
做出一個帶有 Cost 的 adjacency List
然後透過 MinHeap 每次 Pop 出最小的 Cost 還有那個連接點
package sol
import "container/heap"
type AdjacentNode struct {
Cost, Point int
}
type AdjacentMinHeap []AdjacentNode
func (h *AdjacentMinHeap) Len() int {
return len(*h)
}
func (h *AdjacentMinHeap) Less(i, j int) bool {
return (*h)[i].Cost < (*h)[j].Cost
}
func (h *AdjacentMinHeap) Swap(i, j int) {
(*h)[i], (*h)[j] = (*h)[j], (*h)[i]
}
func (h *AdjacentMinHeap) Push(val interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, val.(AdjacentNode))
}
func (h *AdjacentMinHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func abs(value int) int {
if value > 0 {
return value
}
return -value
}
func minCostConnectPoints(points [][]int) int {
// make adjacency map
n := len(points)
adjacencyMap := make(map[int]AdjacentMinHeap, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
point1 := points[i]
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
point2 := points[j]
dist := abs(point1[0]-point2[0]) + abs(point1[1]-point2[1])
adjacencyMap[i] = append(adjacencyMap[i], AdjacentNode{Cost: dist, Point: j})
adjacencyMap[j] = append(adjacencyMap[j], AdjacentNode{Cost: dist, Point: i})
}
}
totalCost := 0
visit := make(map[int]struct{})
priorityQueue := &AdjacentMinHeap{AdjacentNode{Cost: 0, Point: 0}}
heap.Init(priorityQueue)
// Prim's algorithm
for len(visit) < n {
node := heap.Pop(priorityQueue).(AdjacentNode)
if _, exist := visit[node.Point]; exist {
continue
}
totalCost += node.Cost
visit[node.Point] = struct{}{}
adjList := adjacencyMap[node.Point]
for _, adjNode := range adjList {
if _, exist := visit[adjNode.Point]; !exist {
heap.Push(priorityQueue, adjNode)
}
}
}
return totalCost
}- 要理解如何做出 adjacency list
- 要理解 Prim’s algorithm
- 需要從每個點為起點 做出一個 帶有 weight 的 adjacency list
- 每次透過 HashSet 紀錄 visit 過的點
- 然後依序把 adjacency List 的點 放到 minHeap 來找出下一個最小 cost 的點