|
1 | 1 | import RealTimeAgg from 'versionContent/_partials/_real-time-aggregates.mdx'; |
2 | 2 |
|
3 | 3 | In modern applications, data usually grows very quickly. This means that aggregating |
4 | | -it into useful summaries can become very slow. Continuous aggregates in $TIMESCALE_DB make |
5 | | -aggregating data lightning fast, accurate, and easy. |
6 | | - |
7 | | -If you are collecting data very frequently, you might want to aggregate your |
8 | | -data into minutes or hours instead. For example, if an IoT device takes |
| 4 | +it into useful summaries can become very slow. If you are collecting data very frequently, you might want to aggregate your |
| 5 | +data into minutes or hours instead. For example, if an IoT device takes |
9 | 6 | temperature readings every second, you might want to find the average temperature |
10 | 7 | for each hour. Every time you run this query, the database needs to scan the |
11 | | -entire table and recalculate the average. |
| 8 | +entire table and recalculate the average. $TIMESCALE_DB makes aggregating data lightning fast, accurate, and easy. |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +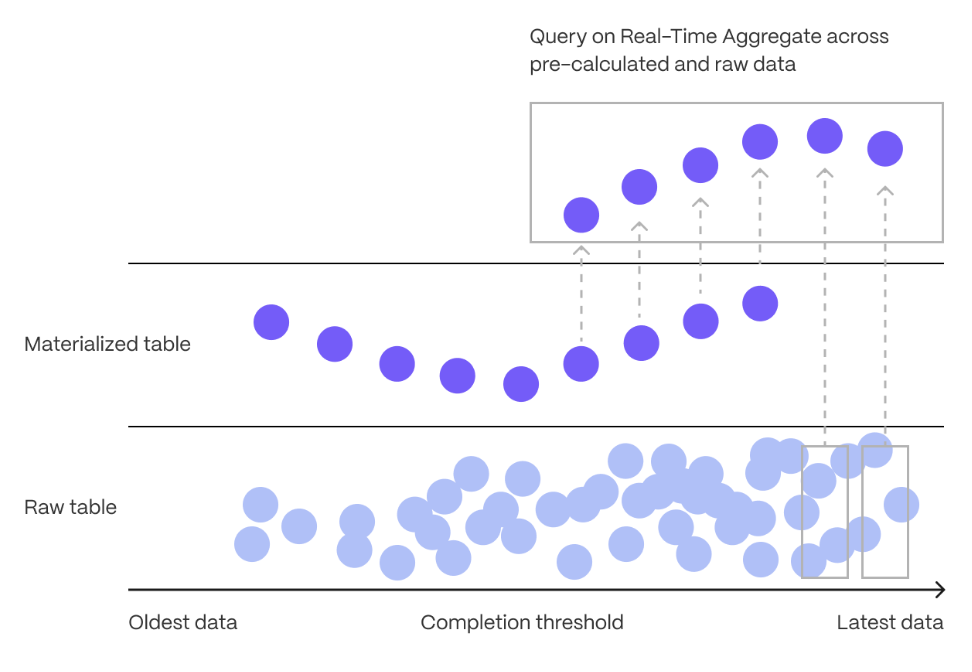 |
12 | 11 |
|
13 | | -Continuous aggregates are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically |
| 12 | +Continuous aggregates in $TIMESCALE_DB are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically |
14 | 13 | in the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your |
15 | 14 | dataset are tracked, and the hypertable behind the continuous aggregate is |
16 | 15 | automatically updated in the background. |
17 | 16 |
|
18 | | -You don't need to manually refresh your continuous aggregates, they are |
19 | | -continuously and incrementally updated in the background. Continuous aggregates |
20 | | -also have a much lower maintenance burden than regular $PG materialized |
| 17 | +Continuous aggregates have a much lower maintenance burden than regular $PG materialized |
21 | 18 | views, because the whole view is not created from scratch on each refresh. This |
22 | 19 | means that you can get on with working your data instead of maintaining your |
23 | 20 | database. |
24 | 21 |
|
25 | | - |
26 | 22 | Because continuous aggregates are based on hypertables, you can query them in exactly the same way as your other tables. This includes continuous aggregates in the rowstore, compressed into the [columnstore][hypercore], |
27 | | -or [tiered to object storage][data-tiering]. You can even create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs] - for an even more fine-tuned aggregation. |
| 23 | +or [tiered to object storage][data-tiering]. You can even create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs], for an even more fine-tuned aggregation. |
28 | 24 |
|
29 | 25 | [Real-time aggregation][real-time-aggregation] enables you to combine pre-aggregated data from the materialized view with the most recent raw data. This gives you up-to-date results on every query. <RealTimeAgg /> |
30 | 26 |
|
|
0 commit comments