-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
User Guide
- Installation
- TranD Overview
- Single Transcriptome Evaluation (TranD 1 GTF)
- Comparison of Two Transcriptomes (TranD 2 GTF)
- Documentation and Script
Installation of TranD can be done in 2 steps.
Create a new conda environment with python (>=3.7) and activate the environment. Note there are two ways to create the environment depending on the location you would like to save the environment.
## To place environment in your default conda environment location
conda create -n TranD_env python=3.8
conda activate TranD_env
## To place environment in a specific location
conda create -p /path/to/conda_envs/TranD_env python=3.8
conda activate /path/to/conda_envs/TranD_env
Install TranD and dependencies. This can be done 3 different ways: A) with pip for most recent PyPI release, B) with conda for most recent conda release (should be same release as in PyPI), or C) clone this github repository to get most recent TranD code (may include updates that have not been released yet).
A) For the most recent PyPI release, activate the new environment and install with pip:
pip install trand
OR
B) For the most recent conda release, activate the new environment and install with conda:
conda install -c bioconda trand
OR
C) For the most recent code in this repository, set up a development environment by cloning the repository:
cd /path/to/github_clones
git clone https://github.com/McIntyre-Lab/TranD.git
Then, change directories (cd) into the source directory of the TranD clone and install TranD using pip:
conda activate TranD
cd /path/to/github_clones/TranD/source
pip install -e .
TranD has 2 overarching modes: 1 GTF or 2 GTF inputs.
In 1-GTF mode, structural differences within a single transcriptome are described and quantified via various output files and plots. In 2-GTF mode, two transcriptomes are compared via various output files and plots.
Below is the TranD help message, which provides an overview of general usage:
usage: trand [-h] [-o OUTDIR] [-x PREFIX] [-l LOG_FILE] [-c]
[-e {pairwise,gene}] [-k] [-p {all,both,first,second}] [-1 NAME1]
[-2 NAME2] [-n CPU_CORES] [-f] [-s] [-i] [-v] [--version]
input_file [input_file ...]
Perform transcript distance, complexity and transcriptome comparison analyses.
positional arguments:
input_file One or two input GTF file(s).
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o OUTDIR, --outdir OUTDIR
Output directory, created if missing. Default: current
directory.
-x PREFIX, --prefix PREFIX
Output prefix of various output files. " Default: no
prefix for 1GTF, 'name1_vs_name2' for 2GTF.
-l LOG_FILE, --logfile LOG_FILE
Log file path and name for logging processing events to file.
-c, --complexityOnly Used with 1 or 2 GTF input file(s). Output only
transcriptome complexity measures. Default: Perform
all analyses and comparisons including complexity
calculations
-e {pairwise,gene}, --ea {pairwise,gene}
Specify type of within gene transcript comparison (event analysis):
pairwise - Used with 1 or 2 GTF input files. Compare
pairs of transcripts within a gene. gene - Used with 1
GTF input file. Compare all transcripts within a gene
Default: pairwise
-k, --keepir Keep transcripts with Intron Retention(s) when
generating transcript events. Only used with 1 GTF
input file. Default: remove
-p {all,both,first,second}, --pairs {all,both,first,second}
Used with 2 GTF input files. The TranD metrics can be
for all transcript pairs in both GTF files or for a
subset of transcript pairs using the following
options: both - Trand metrics for the minimum pairs in
both GTF files, first - TranD metrics for the minimum
pairs in the first GTF file, second - TranD metrics
for the minimum pairs in the second GTF file all -
TranD metrics for all transcript pairs in both GTF
files Default: both
-1 NAME1, --name1 NAME1
Used with 2 GTF input files. User-specified name to be
used for labeling output files related to the first
GTF file. Name must be alphanumeric, can only include
"_" special character and not contain any spaces.
Default: d1
-2 NAME2, --name2 NAME2
Used with 2 GTF input files. User-specified name to be
used for labeling output files related to the second
GTF file. Name must be alphanumeric, can only include
"_" special character and not contain any spaces.
Default: d2
-n CPU_CORES, --cpus CPU_CORES
Number of CPU cores to use for parallelization.
Default: 1
--subset_file
Enter a CSV file of transcript pairs to exclusively process in pairwise mode.
Format: no header, two columns (transcript_1 and transcript_2)
-f, --force Force overwrite existing output directory and files
within.
-s, --skip-plots Skip generation of all plots.
-
-i, --skip-intermediate
Skip intermediate file output (junction and exon
region/fragment files).
-v, --verbose Verbose output
--version Display version
It is very important to note that TranD requires significant time and/or memory to run, especially when comparing two transcriptomes (2GTF mode, and even more so when using the -p both parameter, more information on that below). Below is a list of annotations and some benchmarking information to use as an estimate when running TranD on other PCs.
- 2 GTF Minimum indicates the parameter
-p bothand 2 GTF All indicates-p all
| Annotation(s) | Num Transcripts | TranD Mode | Num CPUs | Max Memory Usage (mb) | Time (hh:mm:ss) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refseq Human Annotation Mapped to Ensembl Coordinates | 165898 | 1 GTF Gene | 64 | 4800.968 | 20:59:38 |
| FlyBase D. mel. Reference Annotation (r6.17) | 35255 | 1 GTF Gene | 64 | 821.56 | 00:35:29 |
| FlyBase D. mel. Reference Annotation (r6.17) | 35255 | 1 GTF Pairwise | 64 | 1836.524 | 01:46:42 |
| Ensembl vs. Refseq, Chromosome 1 | 20492 vs 16075 | 2 GTF All | 64 | 5123.724 | 14:50:06 |
| Ensembl vs. Refseq, Chromosome 2 | 17239 vs 12345 | 2 GTF All | 64 | 4674.92 | 10:05:06 |
| Dros. mel. vs sim. (mapped to mel coordinates) | 33794 vs 41352 | 2 GTF Minimum | 64 | 6037.52 | 23:55:51 |
- Note about human data: Human annotations tend to be very large, so when running with large annotations it is highly recommended to run TranD by chromosome on separate machines (or on a computer cluster via array job). No time is saved through running by chromosome on a single machine. More information on how to do this here.
- This why the above benchmarking information provides parameters on only the 2 longest chromosomes.
- Be sure to allocate more time and memory when running TranD 2 GTF Minimum and 1 GTF Pairwise (for larger annotations).
- For a verbose list of many more runtimes (including all chromosomes for the Human Annotation Comparison), please see our Precomputed Files.
With the input of a single transcriptome (GTF file) TranD can generate 1-GTF analysis in the form of gene-level complexity measures. Gene-level complexity measures are calculated by comparing pairs of transcripts within a gene (‘pairwise’ mode) or by comparing all transcripts within a gene (‘gene’ mode). If ‘gene’ mode is selected then CSV files containing all possible exon regions and exon fragments is created along with a summary plot describing the transcriptome.
Pairwise distances can be calculated for all pairs within a gene and the patterns of splicing (5’/3’ variation, alternate donor/acceptor, alternate exons, intron retentions) as well as the number of nucleotide positions that differ for each metric can summarized.
- If a gene only has one transcript, it will not be included in the analysis files output by TranD (that gene is completely removed during analysis).
- If two transcripts on opposite strands have the same gene identifier, TranD will output a warning and skip comparison of those two transcripts.
trand \
/path/to/transcriptome.gtf \ # transcriptome GTF
-o /path/to/outdir \ # TranD output directory
-f \ # Force output to overwrite existing output directory if running again
-n 8 # Number of CPU (default: 1)
- One GTF file corresponding to the transcriptome of interest. File must contain “exon” features with transcript_id and gene_id values indicated in attributes.
- Full path to output directory, if it does not exist, it will automatically be created. The directory can already exist, and the output files will be replaced if present in directory and
-f(--force) option is set. - Number of CPU to use for parallelization (default: 1, no parallelization). TranD splits by gene to each CPU so if you have many genes with lower numbers of transcripts then increasing this value will help with speed (genes with higher numbers of transcripts may not benefit as well).
-
Optional: Indicator to skip output of intermediate files
-i(--skip-intermediate) and only output the minimum distance output file and all plots. -
Optional: Using either 1 GTF or 2 GTF output,
-c(--complexityOnly) can be used to generate only the complexity measures. -
Optional: Using either 1 GTF or 2 GTF output,
-s(--skip-plots) can be used to skip the generation of any plots/legends. -
Optional: In only pairwise mode, you may select a specific list of transcript pairs to have processed, while the rest are skipped. To do this, enter a CSV file with no header and a list of the pairs in a two column format (transcript_1,transcript_2) with the argument
--subset_file.
- Output CSV file (called
pairwise_transcript_distance.csv). The distance columns are described here. - Box plots of complexity metrics (
complexity_plots.png) and automatically generated figure legend (complexity_plots.rtf) for each transcriptome. - Output CSV file that displays a list of complexity measures (
transcriptome_complexity_counts.csv). - Various plots described in TranD manuscript and automatically generated figure legends for each.
- If intermediate files are output (no
-i): a CSV file of pairwise events generated for each pair is output (event_analysis.csv) and a CSV file of all junctions in the transcriptome with columns for gene_id, transcript_id, and coords (chrom_:_start-10_:_end+9_:_strand, where start coordinate is 0-based) (junction_catalog.csv) is output.
For the rest of the user guide, sample code will be available for clarification on the best usage of TranD. Additionally, sample output will be available for clarification on what each output file truly entails. The sample input for 1 GTF analysis is the full transcriptome (GTF) for Drosophila melanogaster (r6.17) which can be found in Precomputed Files.
1-GTF pairwise sample code:
trand \
./input/dmel-all-r6.17.gtf \
-o ./output/TranD_1GTF_Pairwise \
-f \
-n 8
The sample output can be found here.
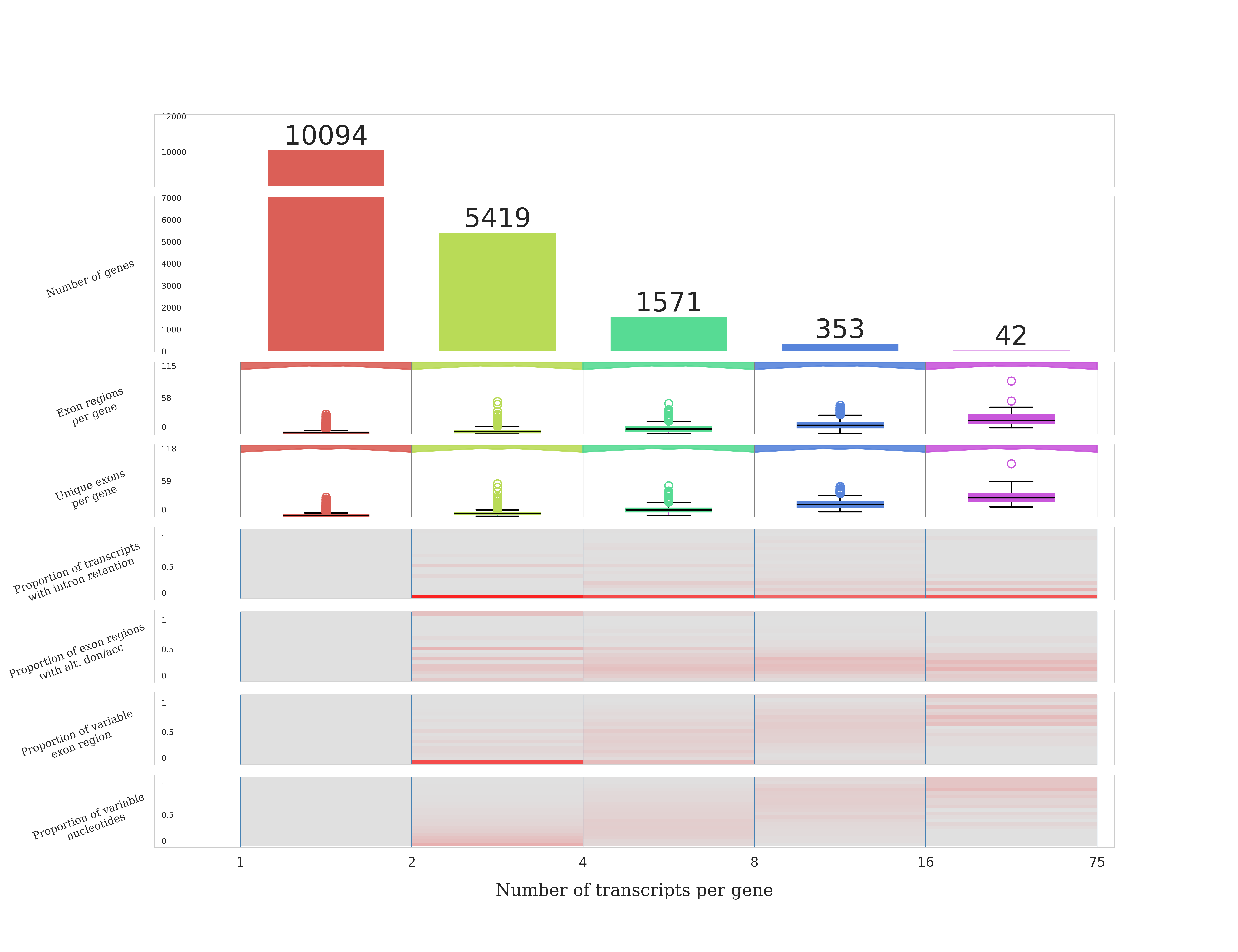
Gene mode compares all transcripts within each gene and outputs a transcriptome summary plot like the example below (D. melanogaster r6.17) and generates exon region and exon fragment event files representing the exonic space of each gene.
trand \
/path/to/transcriptome.gtf \ # transcriptome GTF
-o /path/to/outdir \ # TranD output directory
--ea gene \ # Switch TranD to gene mode
--keepir \ # Keep transcripts with IR events
-f \ # Force output to overwrite existing output directory if running again
-n 8 # Number of CPU (default: 1)
Generates event file by comparing all transcripts for a gene and outputs a transcriptome summary plot.
- Inputs are the same as above
- NOTE: If you want to keep intron retention events, add the argument
-k(--keepir) (If not added, transcripts with intron retention will be removed.)
- Complexity output files described above
- A CSV file of exon regions (
event_analysis_er.csv) - A CSV file of exon fragments (
event_analysis_ef.csv) - A CSV file of transcript_id values (
ir_transcripts.csv) for transcripts with intron retention events when compared to all other transcripts of the gene (NOTE: this file is empty if--keepiris not used) - A CSV file of all junctions in the transcriptome with columns for gene_id, transcript_id, and coords (
chrom_:_start-10_:_end+9_:_strand, where start coordinate is 0-based) (junction_catalog.csv) - A CSV file listing all genes and number of unique exons per gene (
uniq_exons_per_gene.csv). - Plot (
transcriptome_summary_plot.png) and auto-generated figure legend (transcriptome_summary_plot.rtf) for a summary of the transcriptome structure - Plot (
all_gene_prop_nt_variability.png) and auto-generated figure legend (all_gene_prop_nt_variability.rtf) for the distribution of the proportion of nucleotide variability (calculated as the number of nucleotides that are contained in at least one but not all exons of the gene over the total number of nucleotides included in at least one exon of the gene). - Plot (
multi_xcrpt_gene_prop_nt_variability.png) and auto-generated figure legend (multi_xcrpt_gene_prop_nt_variability.rtf) for the distribution of variable nucleotides across multi-transcript genes.
1-GTF gene sample code:
trand \
./input/dmel-all-r6.17.gtf \
-o ./output/TranD_1GTF_Gene \
-e gene \
-k \
-f \
-n 8
The sample output can be found here.
Compare two transcriptomes that are from the same genomic coordinates (both sets of transcript coordinates map to the same genome). This mode of TranD is useful for comparing read methods or comparing species (if the species' annotations have been properly mapped to the same genome).
-
Transcriptomes must have shared gene_id values for transcripts to be compared within each shared gene. This is especially important when comparing two species or different references. This can be done by mapping the two annotations onto the same genome and using GFFCompare. This process is well documented on this wiki for Drosophila and human annotations. Possible errors if gene_ids are not the same:
- This can cause a "No objects to concatenate" error.
- This can also be checked by looking at the (gtf1)vs(gtf2)_gtf1_only.gtf and (gtf1)vs(gtf2)_gtf2_only.gtf files in the output. If these files perfectly match gtf1 and gtf2, it indicates that no transcript pairing was done.
-
Transcriptomes must have the exact same seqids (chromosome numbers) within the annotation. This is also important when comparing two references that use different chromosome number formats (ex: Refseq vs Ensembl). The process for using cthreepo to convert chromosome IDs between human formats is well documented in the human example here on the wiki. Possible errors if seqids are different in each annotation:
- TranD will still run, but there will be several lines (as in, one per transcript pair) that repeat "Multiple contig/chromn locations found for {transcript names}, skipping." either the log file or terminal output.
trand \
/path/to/reads.gtf \ # GTF of first transcriptome
/path/to/ref.gtf \ # GTF of second transcriptome
-o /path/to/outdir \ # TranD output directory
-1 name1 \ # Name for first transcriptome (default: “d1”)
-2 name2 \ # Name for second transcriptome (default: “d2”)
-p both \ # Output option for table of transcript pairs
-i \ # Skip intermediate output files
-f \ # Force output to overwrite existing output directory if running again
-n 8 # Number of CPU (default: 1)
- Two GTF files corresponding to the transcriptomes of interest. Files must contain “exon” features with transcript_id and gene_id values indicated in attributes.
- Names associated with each transcriptome to be used in output tables and plots (default: “d1” and “d2”). Names must be alphanumeric with no spaces or special characters other than “_”.
- Full path to output directory, if it does not exist, it will automatically be created. The directory can already exist, and the output files will be replaced if present in directory and
-f(--force) option is set. -
-p: Output category option allows user to select the output table of transcript pairs to only be minimum pairs from the “first” transcriptome, only minimum pairs from the “second” transcriptome, minimum pairs for “both” transcriptomes (minimum pair in either), or output “all” pairwise transcript pairs regardless of minimum pair classification. (Default: “both”) - Number of CPU to use for parallelization (default: 1, no parallelization). TranD splits by gene to each CPU so if you have many genes with lower numbers of transcripts then increasing this value will help with speed (genes with higher numbers of transcripts may not benefit as well).
-
Optional: Indicator to skip output of intermediate files
-i(--skip-intermediate) and only output the minimum distance output file and all plots. -
Optional: Using either 1 GTF or 2 GTF output,
-c(--complexityOnly) can be used to generate only the complexity measures. -
Optional: Using either 1 GTF or 2 GTF output,
-s(--skip-plots) can be used to skip the generation of any plots/legends.
- Output CSV file
-
pairwise_transcript_distance.csvif-pis “all” OR -
minimum_pairwise_transcript_distance.csvif-pis "both", "first", or "second"
-
- If
-p all: The output CSV file includes the transcript distance output for all pairwise transcripts pairs (“all”), - If
p (both/first/second): The output CSV file includes the minimum distance output for all minimum pairs of the first transcriptome to the second transcriptome (“first”), all minimum pairs of the second transcriptome to the first transcriptome (“second”), or the minimum pairs for either the first transcriptome and/or the second transcriptome (“both”).
The pairwise distance columns are described in here. The additional columns added to the pairwise distance file when using minimum mode are described here.
2. Box plots of complexity metrics ([name]_complexity_plots.png) and automatically generated figure legend ([name]_complexity_plots.rtf) for each transcriptome, where [name] represents the names given to each transcriptome (or “d1” and “d2” as default).
3. Various plots described in TranD manuscript and automatically generated figure legends for each.
4. Output CSV file that displays a list of complexity measures for each transcriptome ([name]_complexity_counts.csv).
4. If intermediate files are output (no -i), CSV file of pairwise events generated for each pair is output (event_analysis.csv).
The sample input for 2 GTF analysis are the transcriptomes of D. melanogaster (GTF) and D. simulans (GTF), mapped onto the genome of D. melanogaster, and subset to only the coding genes. The GTFs are referred to as mel2mel and sim2mel, respectively (based on the "mel" and "sim" species mapped to the "mel" genome). The process of creating these mapped GTFs is similar to the process found in the Drosophila Species Comparison.
2-GTF sample code:
trand \
./input/mel2mel_coding_associated_gene.gtf \
./input/sim2mel_coding_associated_gene.gtf \
-o ./output/TranD_2GTF_Pairwise \
-1 mel2mel \
-2 sim2mel \
-p both \
-i \
-f \
-n 8
The sample output can be found here.
Documentation and Script used for generating all of the sample output are in the links provided.