kubesdk is a modern, async-first Kubernetes client and API model generator for Python.
- Developer-friendly, with fully typed APIs so IDE auto-complete works reliably across built-in resources and your custom resources.
- Made for large multi-cluster workloads.
- Minimal external dependencies (client itself depends on
aiohttpandPyYAMLonly).
The project is split into three packages:
The core client library, which you install and use in your project.
Pre-generated Python models for all upstream Kubernetes APIs, for every Kubernetes version 1.23+. All Kubernetes APIs are bundled under a single kube-models package version, so you don’t end up in model-versioning hell.
Separate models package gives you ability to use latest client version with legacy Kubernetes APIs and vice versa.
You can find the latest generated models here. They are automatically uploaded to an external repository to avoid increasing the size of the main kubesdk repo.
CLI that generates models from a live cluster or OpenAPI spec, including your own CRDs.
| Feature / Library | kubesdk | kubernetes-asyncio | Official client (kubernetes) |
kr8s | lightkube |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Async client | ✅ | ✅ | ✗ | ✅ | ✅ |
| IDE-friendly client methods typing | ✅ Full | ◑ Partial | ◑ Partial | ◑ Partial | ✅ Good |
| Typed models for all built-in APIs | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ◑ Partial | ✅ |
| Built-in multi-cluster ergonomics | ✅ | ◑ Manual | ◑ Manual | ◑ Manual | ◑ Manual |
| Easy API model generation (CLI) | ✅ | ✗ | ✗ | ◑ | ◑ |
| High-level JSON Patch helpers (typed) | ✅ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| One API surface for core + CRDs | ✅ | ✗ | ✗ | ◑ | ✅ |
| Separated API models package | ✅ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✅ |
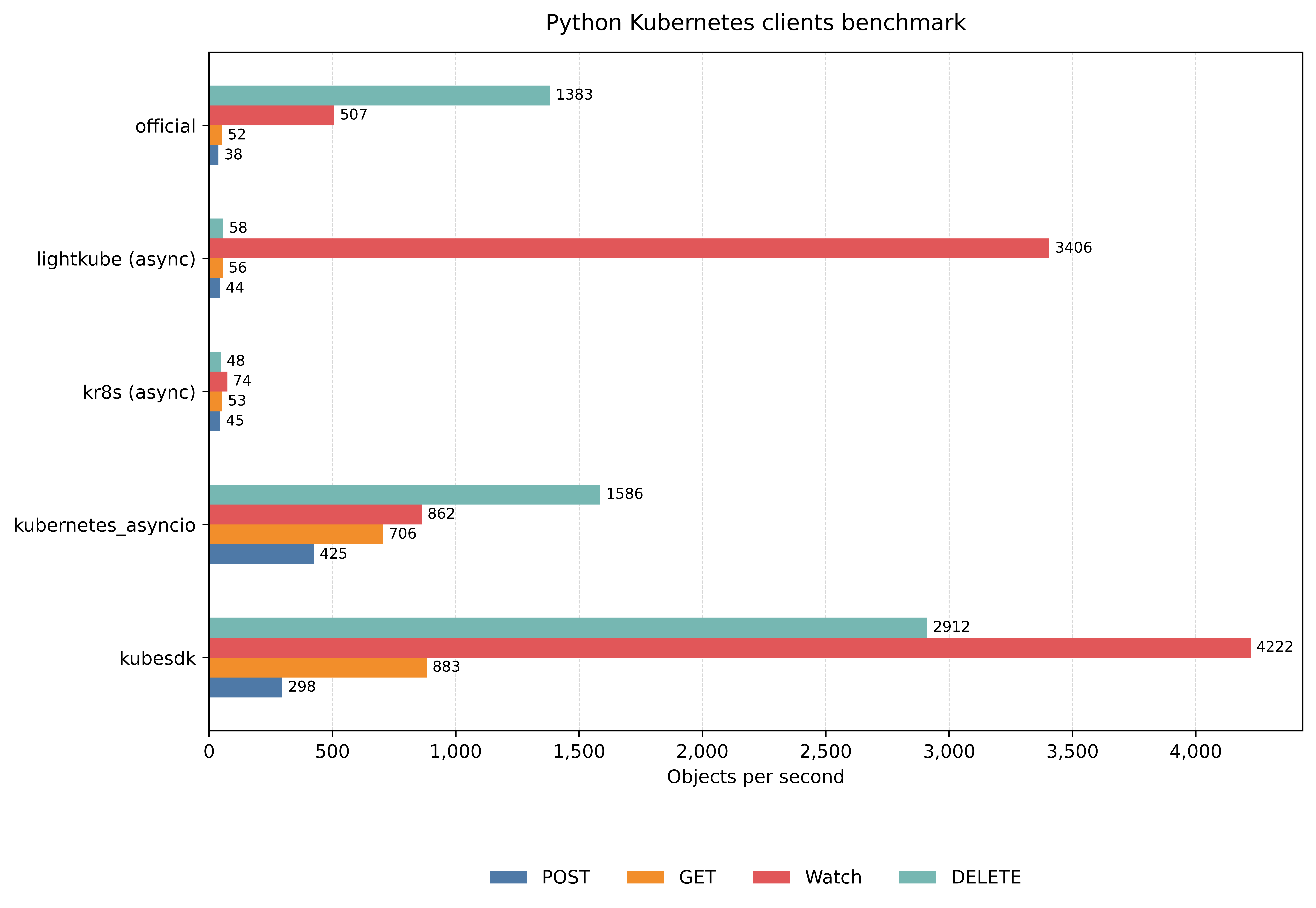
| Performance on large-scale workloads | ✅ >1000 RPS | ✅ >1000 RPS | <100 RPS | <100 RPS | <100 RPS |
Benchmark results were collected against kind (Kubernetes in Docker), which provides a fast, consistent local environment for comparing client overhead under the same cluster conditions.
pip install kubesdk[cli]import asyncio
from kube_models.apis_apps_v1.io.k8s.api.apps.v1 import (
Deployment,
DeploymentSpec,
LabelSelector,
)
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.api.core.v1 import (
PodTemplateSpec,
PodSpec,
Container,
)
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.apimachinery.pkg.apis.meta.v1 import ObjectMeta
from kubesdk import login, create_k8s_resource, get_k8s_resource
async def main() -> None:
# Load available cluster config and establish cluster connection process-wide
await login()
deployment = Deployment(
metadata=ObjectMeta(name="example-nginx", namespace="default"),
spec=DeploymentSpec(
replicas=2,
selector=LabelSelector(matchLabels={"app": "example-nginx"}),
template=PodTemplateSpec(
metadata=ObjectMeta(labels={"app": "example-nginx"}),
spec=PodSpec(
containers=[
Container(
name="nginx",
image="nginx:stable",
)
]
),
),
),
)
# Create the Deployment
await create_k8s_resource(deployment)
# Read it back
created = await get_k8s_resource(Deployment, "example-nginx", "default")
# IDE autocomplete works here
print("Container name:", created.spec.template.spec.containers[0].name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())import asyncio
from kube_models.apis_apps_v1.io.k8s.api.apps.v1 import Deployment
from kubesdk import login, watch_k8s_resources
async def main() -> None:
await login()
async for event in watch_k8s_resources(Deployment, namespace="default"):
deploy = event.object
print(event.type, deploy.metadata.name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())import asyncio
from kube_models.apis_apps_v1.io.k8s.api.apps.v1 import Deployment
from kubesdk import login, delete_k8s_resource
async def main() -> None:
await login()
await delete_k8s_resource(Deployment, "example-nginx", "default")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())from dataclasses import replace
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.api.core.v1 import LimitRange, LimitRangeSpec, LimitRangeItem
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.apimachinery.pkg.apis.meta.v1 import OwnerReference, ObjectMeta
from kubesdk import create_k8s_resource, update_k8s_resource, from_root_, path_, replace_
async def patch_limit_range() -> None:
"""
Example: bump PVC min storage and add an OwnerReference in a single,
server-side patch. kubesdk will compute the diff between `latest` and
`updated` and pick the best patch type (strategic/merge) automatically.
"""
# Create the initial LimitRange object.
namespace = "default"
initial_range = LimitRange(
metadata=ObjectMeta(
name="example-limit-range",
namespace=namespace,
),
spec=LimitRangeSpec(
limits=[
LimitRangeItem(
type="PersistentVolumeClaim",
min={"storage": "1Gi"},
)
]
),
)
# The client returns the latest version from the API server.
latest: LimitRange = await create_k8s_resource(initial_range)
#
# We want to make a few modifications, will do them one by one.
# First, append a new OwnerReference.
#
# IDE autocomplete works here
owner_ref_path = path_(from_root_(LimitRange).metadata.ownerReferences)
updated_range = replace_(
latest,
# IDE autocomplete works here
path=owner_ref_path,
# Typecheck works here
new_value=latest.metadata.ownerReferences + [
OwnerReference(
uid="9153e39d-87d1-46b2-b251-5f6636c30610",
apiVersion="v1",
kind="Secret",
name="test-secret-1",
),
]
)
#
# Then, set a new list of limits with updated PVC min storage.
#
# IDE autocomplete works here
limits_path = path_(from_root_(LimitRange).spec.limits)
updated_range = replace_(
updated_range,
# IDE autocomplete works here
path=limits_path,
# Typecheck works here
new_value=[
replace(lim, min={"storage": "3Gi"})
if lim.type == "PersistentVolumeClaim" else lim
for lim in latest.spec.limits
]
)
update_all_changed_fields = True
# Let kubesdk compute the diff and patch everything that changed
if update_all_changed_fields:
await update_k8s_resource(updated_range, built_from_latest=latest)
# Or, restrict the patch to specific paths only (optional)
else:
await update_k8s_resource(
updated_range,
built_from_latest=latest,
paths=[owner_ref_path, limits_path],
)import asyncio
from dataclasses import replace
from kubesdk import login, KubeConfig, ServerInfo, watch_k8s_resources, create_or_update_k8s_resource, \
delete_k8s_resource, WatchEventType
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.api.core.v1 import Secret
async def sync_secrets_between_clusters(src_cluster: ServerInfo, dst_cluster: ServerInfo):
src_ns, dst_ns = "default", "test-kubesdk"
async for event in watch_k8s_resources(Secret, namespace=src_ns, server=src_cluster.server):
if event.type == WatchEventType.ERROR:
status = event.object
raise Exception(f"Failed to watch Secrets: {status.data}")
# Optional
if event.type == WatchEventType.BOOKMARK:
continue
# Sync Secret on any other event
src_secret = event.object
if event.type == WatchEventType.DELETED:
# Try to delete, skip if not found
await delete_k8s_resource(
Secret, src_secret.metadata.name, dst_ns, server=dst_cluster.server, return_api_exceptions=[404])
continue
dst_secret = replace(
src_secret,
metadata=replace(src_secret.metadata, namespace=dst_ns,
# Drop all k8s runtime fields
uid=None,
resourceVersion=None,
managedFields=None))
# If the Secret exists, a patch is applied; if it doesn't, it will be created.
await create_or_update_k8s_resource(dst_secret, server=dst_cluster.server)
print(f"Secret {dst_secret.metadata.name} has been synced "
f"from `{src_ns}` ns in {src_cluster.server} to `{dst_ns}` ns in {dst_cluster.server}")
async def main():
default = await login()
eu_finland_1 = await login(kubeconfig=KubeConfig(context_name="eu-finland-1.clusters.puzl.cloud"))
# Endless syncing loop
while True:
try:
await sync_secrets_between_clusters(default, eu_finland_1)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
await asyncio.sleep(5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())You can generate your custom resource models from your Kubernetes cluster API directly using CLI. Another option is to define them manually. Below is the example of a FeatureFlag CR.
A FeatureFlag CR is a simple k8s resource that drives a progressive rollout by updating Nginx Ingress canary annotations (assumed you are using Nginx).
- Operator watches
FeatureFlagobjects and setsnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary=trueandnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight=<0..100>on the referencedspec.canary_ingress. - When the flag is disabled or resource is deleted, the operator forces the canary weight to
0(no canary traffic).
# operator.py
from __future__ import annotations
import asyncio
from dataclasses import dataclass
from kubesdk import login, watch_k8s_resources, update_k8s_resource, WatchEventType, path_, from_root_, replace_, \
K8sAPIRequestLoggingConfig
from kubesdk.crd import CustomK8sResourceDefinition, CustomK8sResource, crd_field, PrinterColumn, CRDFieldSpec
from kube_models import Loadable
from kube_models.api_v1.io.k8s.apimachinery.pkg.apis.meta import ObjectMeta
from kube_models.apis_networking_k8s_io_v1.io.k8s.api.networking.v1 import Ingress
# Log each API request
from kubesdk.client import DEFAULT_LOGGING
DEFAULT_LOGGING.on_success = True
@dataclass(kw_only=True, frozen=True, slots=True)
class FeatureFlagSpec(Loadable):
# You can use standard k8s property settings in CRDFieldSpec
enabled: bool = crd_field(spec=CRDFieldSpec(default=False))
rollout_percent: int = crd_field(spec=CRDFieldSpec(minimum=0, maximum=100, default=0))
# Name of the canary Ingress (points to canary Service)
# PrinterColumn will show this field's value in `Ingress` column in kubectl output
canary_ingress: str = crd_field(spec=CRDFieldSpec(printer_column=PrinterColumn(name="Ingress")))
@dataclass(kw_only=True, frozen=True, slots=True)
class FeatureFlagV1Alpha1(CustomK8sResource):
is_namespaced_ = True
group_ = "my-beautiful-saas.com"
plural_ = "featureflags"
apiVersion = f"{group_}/v1alpha1"
kind = "FeatureFlag"
spec: FeatureFlagSpec
@dataclass
class FeatureFlagCRD(CustomK8sResourceDefinition):
versions = [FeatureFlagV1Alpha1]
crd_short_names_ = ["ff"]
async def operator():
finalizer_name = FeatureFlagV1Alpha1.group_
await login()
async for event in watch_k8s_resources(FeatureFlagV1Alpha1):
if event.type == WatchEventType.BOOKMARK:
continue
flag, meta = event.object, event.object.metadata
deleting = meta.deletionTimestamp is not None
actually_enabled = False if deleting or event.type == WatchEventType.DELETED else flag.spec.enabled
weight = int(flag.spec.rollout_percent or 0) if actually_enabled else 0
# Add finalizer on create/normal updates (so we clean up on delete safely)
fin_path = path_(from_root_(FeatureFlagV1Alpha1).metadata.finalizers)
if not deleting and event.type != WatchEventType.DELETED and finalizer_name not in meta.finalizers:
new_finalizers = meta.finalizers + [finalizer_name]
updated_flag = replace_(flag, fin_path, new_finalizers)
await update_k8s_resource(updated_flag, paths=[fin_path]) # patch finalizers only
new_annotations = {
"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary": "true",
"nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight": str(weight)
}
desired_ingress = Ingress(metadata=ObjectMeta(
name=flag.spec.canary_ingress,
namespace=meta.namespace,
annotations=new_annotations
))
annotations_path = path_(from_root_(Ingress).metadata.annotations) # patch annotations only
await update_k8s_resource(desired_ingress, paths=[annotations_path])
# On delete: remove finalizer so the CR can be deleted
if deleting and finalizer_name in meta.finalizers:
new_finalizers = [f for f in meta.finalizers if f != finalizer_name]
updated_flag = replace_(flag, fin_path, new_finalizers)
do_not_log_404 = K8sAPIRequestLoggingConfig(not_error_statuses=[404])
await update_k8s_resource(updated_flag, paths=[fin_path], return_api_exceptions=[404], log=do_not_log_404)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(operator())Before running the operator, you need to generate and apply your CRD in the Kubernetes cluster. Call generator in the dir with your operator.py from above:
kubesdk generate crd --from-dir . --output ./my-crd
kubectl apply -f ./my-crd/featureflags.my-beautiful-saas.yaml- Create demo
Ingressresource
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: checkout-canary
namespace: default
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: checkout-canary.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: dummy-service
port:
number: 80kubectl apply -f checkout-canary-ingress.yaml- Apply your
FeatureFlagcustom resource spec into cluster
apiVersion: my-beautiful-saas.com/v1alpha1
kind: FeatureFlag
metadata:
name: checkout-canary # the same as Ingress metadata.name
namespace: default # in the same namespace
spec:
enabled: true
rollout_percent: 20
canary_ingress: checkout-canarykubectl apply -f checkout-canary-feature-flag.yaml- Check both annotations' values
kubectl get ingress checkout-canary -n default -o jsonpath="{.metadata.annotations.nginx\.ingress\.kubernetes\.io/canary}{'\n'}{.metadata.annotations.nginx\.ingress\.kubernetes\.io/canary-weight}{'\n'}"The command must return
true
20
Generate models directly from a live cluster OpenAPI:
kubesdk generate models \
--url https://my-cluster.example.com:6443 \
--output ./kube_models \
--module-name kube_models \
--http-headers "Authorization: Bearer $(cat /path/to/token)" \
--skip-tls